Welcome to the ABC online training platform
Launched in 2012 by hugely experienced Bar Clerk Bill Conner to provide recruitment and training for Chambers, ABC are totally committed to delivering a client-focused training service and maintaining a reputation for trust, reliability and compliance.
Please contact us if you need any assistance or have any comments or queries on our courses.
Once you have successfully completed the course and final quiz you will see a short questionnaire. We welcome and appreciate your feedback and any suggestions for other Chambers-specific courses.
How to Login
You can access your training account at: https://learn.abcllp.com/
Unless you have been notified otherwise, your username will be your Chambers e-mail address, and a temporary password of ABCtraining123# will have been set.
NB. Please ensure you change this password to one of your choosing when you first log in. You can do this under ‘Learner Profile’, ‘Edit profile’.
If you have any difficulty logging in, you can request a password reset via the “Lost your Password?” link on the login page. The ABC team are also on hand to help by emailing [email protected]
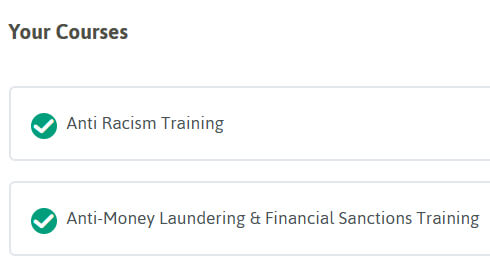
Learner Profile
A list of courses you have a licence for will be shown under ‘Learner Profile’ in alphabetical order. Clicking on the course name will take you into the training.
Your course is presented in a linear fashion, so you must finish each sub-section before it allows you to move onto the next. You can leave and rejoin the module where you left off at any time and via different devices. Once the module is completed, you can revisit the module and move around the sections in any order you wish.
You can revisit the course as many times as you need to during the lifetime of the licence.
After completion, you can even retake the course again if you wish, including the final quiz.

Final Quiz
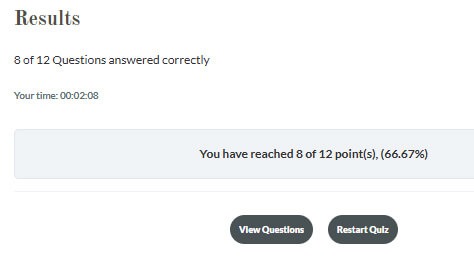
At the end of the training, you will be asked to take a quiz. The required pass mark is 80%.
If you fail the quiz, you will have the opportunity to retake it. You can review your answers to see which questions were answered correctly or incorrectly by selecting ‘View Questions’, before restarting the quiz.
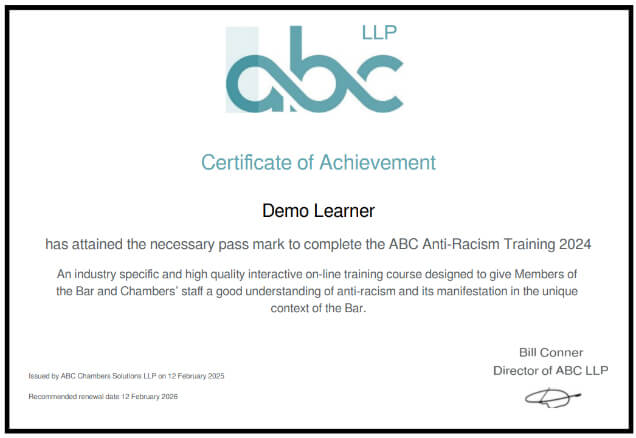
Certificates and Badges
Upon successful completion of a quiz, you will be able to download a certificate.
You can also download a badge to add to your email signature.
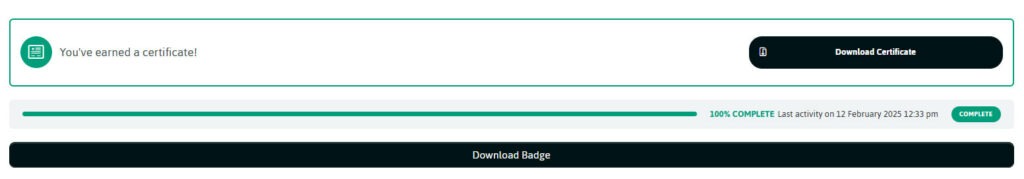
NB. The certificate is automatically emailed to you and the Group Manager.